Footwear Advice
Our main focus on footwear would be for our clients who take part in running as an activity, but we can advise and recommend appropriate footwear after taking into consideration the individual’s foot type, activity level and occupation.
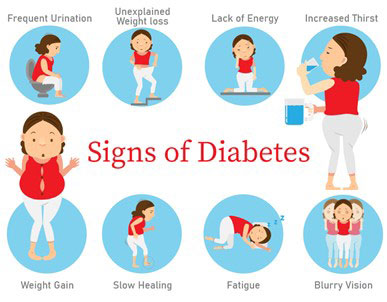
Diabetes
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic illness that occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin, it produces. Hyperglycemia, or raised blood sugar, is a common effect of uncontrolled diabetes and over time leads to serious damage to many of the body’s systems especially the nerves and blood vessels.
Neuropathy
Diabetic foot conditions develop from a combination of causes including poor circulation and neuropathy. Diabetic Neuropathy can cause insensitivity or a loss of ability to feel pain, heat, and cold. Neuropathy can result in patients to develop minor cuts, scrapes, blisters, or pressure sores that they may not be aware of due to the insensitivity. If these minor injuries are left untreated, complications may result and lead to ulceration and possibly even amputation. Neuropathy can also cause deformities such as Bunions, Hammer Toes, and Charcot Feet. It is very important for diabetics to take the necessary precautions to prevent all foot related injuries. Due to the consequences of neuropathy, daily observation of the feet is critical. Preventative foot care measures, reduces the risks of serious foot conditions.
Poor Circulation
Diabetes can lead to peripheral vascular disease that inhibits blood circulation. narrowing of the arteries leads to decreased circulation in the lower part of the legs and the feet. Poor circulation contributes to diabetic foot problems by reducing the amount of oxygen and nutrition supplied to the skin and other tissue, causing injuries to heal poorly. Poor circulation can also lead to swelling and dryness of the foot. Preventing foot complications is more critical for the diabetic patient because poor circulation impairs the healing process and can lead to ulcers, infection, and other serious foot conditions.
Proper footcare is especially critical for diabetics because they are prone to foot problems such as:
- Loss of feeling in their feet
- Changes in the shape of their feet
- Foot ulcers or sores that do not heal
General Footcare
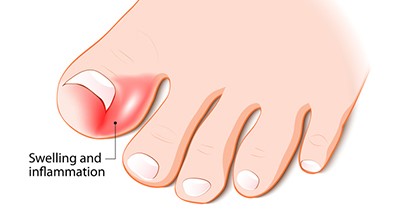
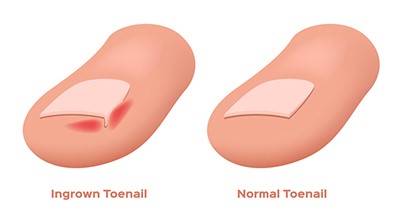
Ingrown Nails
This is a condition whereby the nail grows into the side on your skin causing discomfort, pain, inflammation and in severe cases an infection. This can be treated using two methods: conservative treatment or removal of the nail section with a ‘nail wedge resection’. An ingrown nail can also be prevented by correct nail cutting; correct footwear and wearing open shoes/ airing for your feet.
We perform both procedures in our practices.
Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is the result of damage to the tough band of tissue (fascia) that runs under the sole of the foot, which causes pain in the heel. It most commonly affects people aged 40 to 60 who are overweight or on their feet for long periods of time.
The pain tends to develop gradually over time and is at its worst when you wake up in the morning and at the end of the day.
Resting your heel, regular stretching, applying ice packs, taking painkillers and wearing well-fitted, supportive shoes can often help relieve the pain. In a small number of cases, other treatments such as physiotherapy or injections may be necessary. Rarely, surgery may be required.

Fungal Infections
Fungal infections are among the most common infections seen by a podiatrist. Podiatrists are involved in treating two types of fungal infections:
- Infections of the skin of the feet (tinea pedis) commonly known as athletes foot.
Common signs & symptoms may include an itching/burning sensation of the feet, redness, peeling of the skin, malodor and sometimes even blistering.
- Infections of the nail bed and nail plate known as onychomycosis.
The infected nail often becomes thickened, brittle/crumbly, distorted in shape and discolored. The infected nails generally have an unpleasant appearance. It may lead to malodor of the foot including the socks and shoes.
Risks and predisposing factors for fungal infections include:
Fungal infections love warm, moist, and closed environments and there they thrive in such environments.
Flat Feet
You have flatfeet when the arches on the inside of your feet are flattened, allowing the entire soles of your feet to touch the floor when you stand up.
A common and usually painless condition, flatfeet can occur when the arches don’t develop during childhood. In other cases, flatfeet develop after an injury or from the simple wear-and-tear stresses of age.
Flatfeet can sometimes contribute to problems in your ankles and knees because the condition can alter the alignment of your legs. If you are not having pain, no treatment is usually necessary for flatfeet.
To view the mechanics of your feet, your doctor will observe your feet from the front and back and ask you to stand on your toes. He or she might also look at the wear pattern on your shoes.
Shin Splints
The term “shin splints” refers to pain along the shin bone (tibia) — the large bone in the front of your lower leg. Shin splints are common in runners, dancers and military recruits.
Medically known as medial tibial stress syndrome, shin splints often occur in athletes who have recently intensified or changed their training routines. The increased activity overworks the muscles, tendons and bone tissue.
Most cases of shin splints can be treated with rest, ice and other self-care measures. Wearing proper footwear and modifying your exercise routine can help prevent shin splints from recurring.
Shin splints are usually diagnosed based on your medical history and a physical exam. In some cases, an X-ray or other imaging studies can help identify other possible causes for your pain, such as a stress fracture.
Morton’s Neuroma
Morton’s neuroma is a painful condition that affects the ball of your foot, most commonly the area between your third and fourth toes. Morton’s neuroma may feel as if you are standing on a pebble in your shoe or on a fold in your sock.
Morton’s neuroma involves a thickening of the tissue around one of the nerves leading to your toes. This can cause a sharp, burning pain in the ball of your foot. Your toes also may sting, burn or feel numb.
High-heeled shoes have been linked to the development of Morton’s neuroma. Many people experience relief by switching to lower heeled shoes with wider toe boxes. Sometimes corticosteroid injections or surgery may be necessary.
Achilles Tendinitis
Achilles’ tendinitis is an overuse injury of the Achilles (uh-KILL-eez) tendon, the band of tissue that connects calf muscles at the back of the lower leg to your heel bone.
Achilles’ tendinitis most commonly occurs in runners who have suddenly increased the intensity or duration of their runs. It is also common in middle-aged people who play sports, such as tennis or basketball, only on the weekends.
Most cases of Achilles tendinitis can be treated with relatively simple, at-home care unde your doctor’s supervision. Self-care strategies are usually necessary to prevent recurring episodes. More-serious cases of Achilles tendinitis can lead to tendon tears (ruptures) that may require surgical repair.
During the physical exam, your doctor will gently press on the affected area to determine the location of pain, tenderness or swelling. He or she will also evaluate the flexibility, alignment, range of motion and reflexes of your foot and ankle.
Pediatric podiatry
Pediatric podiatry is an area of podiatry focusing on the treatment of children and the various holistic afflictions that can affect a young person’s lower limbs. Proper care is important in the long term because unattended structural problems with the feet can worsen overtime, eventually causing severe issues with gait and pain. By correcting early foot deformities many long term chronic mobility issues can be safely and effectively addressed, sparing a great deal of discomfort on the part of the patient, and future expenses.
These can include structural issues with the foot like:
- Flat Feet
- Knock Knees
- In-Toeing / Pigeon Toed Gait
- Heel Pain (Sever’s Disease)
- Ingrown Toenails
- Plantar Warts (Verruca Pedis)
- Hypotonia (Low Muscle Tone)
A child’s foot is more at risk compared with an adult. Biomechanical abnormalities as a child can cause long term damage, this is because the foot is more malleable. Children tend to have a high pain threshold as they are easily distracted, and ill-fitting footwear is also an issue when it comes to children’s foot health.